GIS queries allow sewer inspection teams to quickly review specific data and better understand the location and condition of a pipe section or sewer system. They are user-initiated requests to translate data points into actionable information.
In WinCan VX, GIS queries provide seamless transfer of data from WinCan to Esri’s ArcGIS. It starts as operators collect, code and store data in their WinCan database, where it can later be accessed by both platforms as needed. WinCan VX’s GIS query tool allows users to quickly navigate datasets that are relevant to their GIS analysis and asset management database. Users can pose complex queries and filter results to extract insights from large quantities of inspection data. These tools interface seamlessly with Esri’s ArcGIS to help users visualize sewer condition, draft maintenance budgets and allocate resources.

Why Conduct a GIS Query?
Sewer inspection teams conduct GIS queries for a variety of reasons. In some cases, it is used to identify all sections with a specific rating within a neighborhood. Other times, it can be used to review pipe proximity to other assets or hazards. GIS queries are also helpful for tracking down all defects within a specific range of an asset or observation. No matter the focus, the goal of a GIS query is always the same: analyze a subset of WinCan data with a mapping platform like Esri.
Once it’s in a map view, these query results can then be used to create heat maps for fast, visual identification of defect clusters and other trends. Esri’s ArcGIS comes with a variety of symbology and color-coding features, allowing users to get more out of heat maps by specifying attributes or locations. For instance, users could identify where there is a cluster of roots and where surface vegetation may be contributing to the problem. These lines of data are also populated directly in ArcGIS, making it easy to quickly reference pipe numbers, observation photos and inspection media.
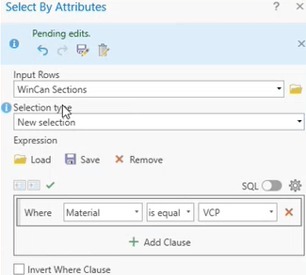
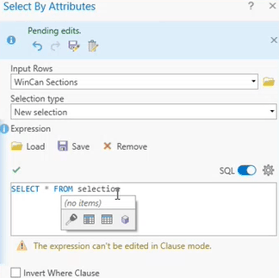
Select By Attribute
The most popular approach for conducting GIS queries is to use the Select By Attribute feature in ArcGIS to pull specific inspection data based on pre-built selection types as shown on the left or customized Structured Query Language (SQL) clauses as shown on the right.
Select By Location
The Select By Location tool provides a similar interface for users to analyze WinCan data, and these results are based on proximity to a selected feature. In example, an operator may want to see how many root infiltrations there are spiraling out from a collection of large oak trees on the surface. Querying by location allows the user to set an anchor feature, a relationship type, as well as a search distance.
How Does a GIS Query Work Behind the Scenes?
WinCan contains all its data within database files that are stored on the local drive where WinCan VX is installed. When Esri queries WinCan for a specific set of data, it accesses the file location and database associated with that data set. It translates the WinCan data into an Esri database, making it readable and accessible by ArcGIS.
Learn more about WinCan’s querying and mapping capabilities by requesting a free demo of WinCan VX:





