Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) are computer systems that collect, store, manage and analyze data relevant to precise locations on Earth. They are the backbone of humankind’s most powerful mapping solutions, and they allow us to gather accurate information about the location of infrastructure in real-time.
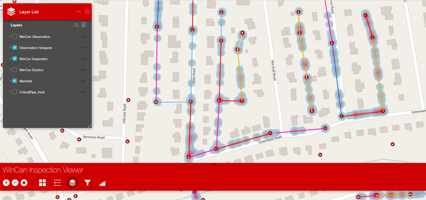
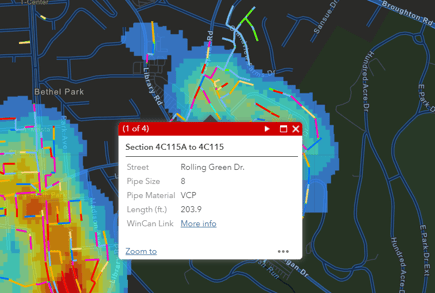
On November 17, the world observes GIS day, a celebration of all things geospatial. Engineers and educators come together to share knowledge and passion for GIS. At WinCan, we see it as an opportunity to celebrate our partnership with Esri, the GIS mapping powerhouse that has revolutionized communities’ understanding of wastewater infrastructure and connected sewer data with other city-wide assets. Geospatial data has changed the way we conduct sewer inspections and analyze observation data. Both operators and engineers rely on the connectivity between WinCan VX and Esri’s ArcGIS because it creates a smooth transition of data from one database to the next. These days, many municipalities would struggle to function without a GIS system to monitor and assess infrastructure.
What Exactly is GIS?
GIS is a broad term for systems designed to create, store, manage and process spatial data. Most often, however, this data is managed and used in the form of an intricate, interactive map. GIS maps are jam-packed with infrastructure data, terrain data, demographic data, and a variety of other essential data points that municipalities rely on to function.
GIS commonly breaks down into 3 core layers: street data, building data and vegetation data. But when each of these layers is filled with information, cities can begin to see a vast array of correlations that help them better understand how the landscape, population, industry and climate impact infrastructure. When the layers are integrated, the result is a digital twin of a city in the form of a map, clearly showing accurate measurement and location of every asset in the municipality.
On a national level, the United States government uses GIS data in creating policies, developing technology and storing spatial data relevant to everything from national security to environmental protection. But smaller industries and local utilities put GIS to good use as well, and it plays an important role in creating the complex asset management systems municipalities rely on to make decisions impacting the everyday lives of their residents.
How Does GIS Support Sewer Inspection?
The most influential aspect of GIS in the wastewater industry is its ability to correlate sewer system condition and location with surrounding and interconnected infrastructure. City planning used to be done entirely on paper, but GIS provides an entirely digital solution, allowing sewer teams to bring valuable inspection data into a map-view for in-depth analysis. For instance, WinCan’s bi-directional integration with Esri’s ArcGIS allows users to automatically transfer NASSCO-certified observations and other infrastructure data from one platform to the other. This ensures that municipalities can review all of their asset data at once and accurately plan maintenance and budget, prioritizing pipe sections in critical condition and conducting inspections according to a more logical workflow.
Learn more about WinCan’s integration with Esri’s ArcGIS by scheduling a demo:





